
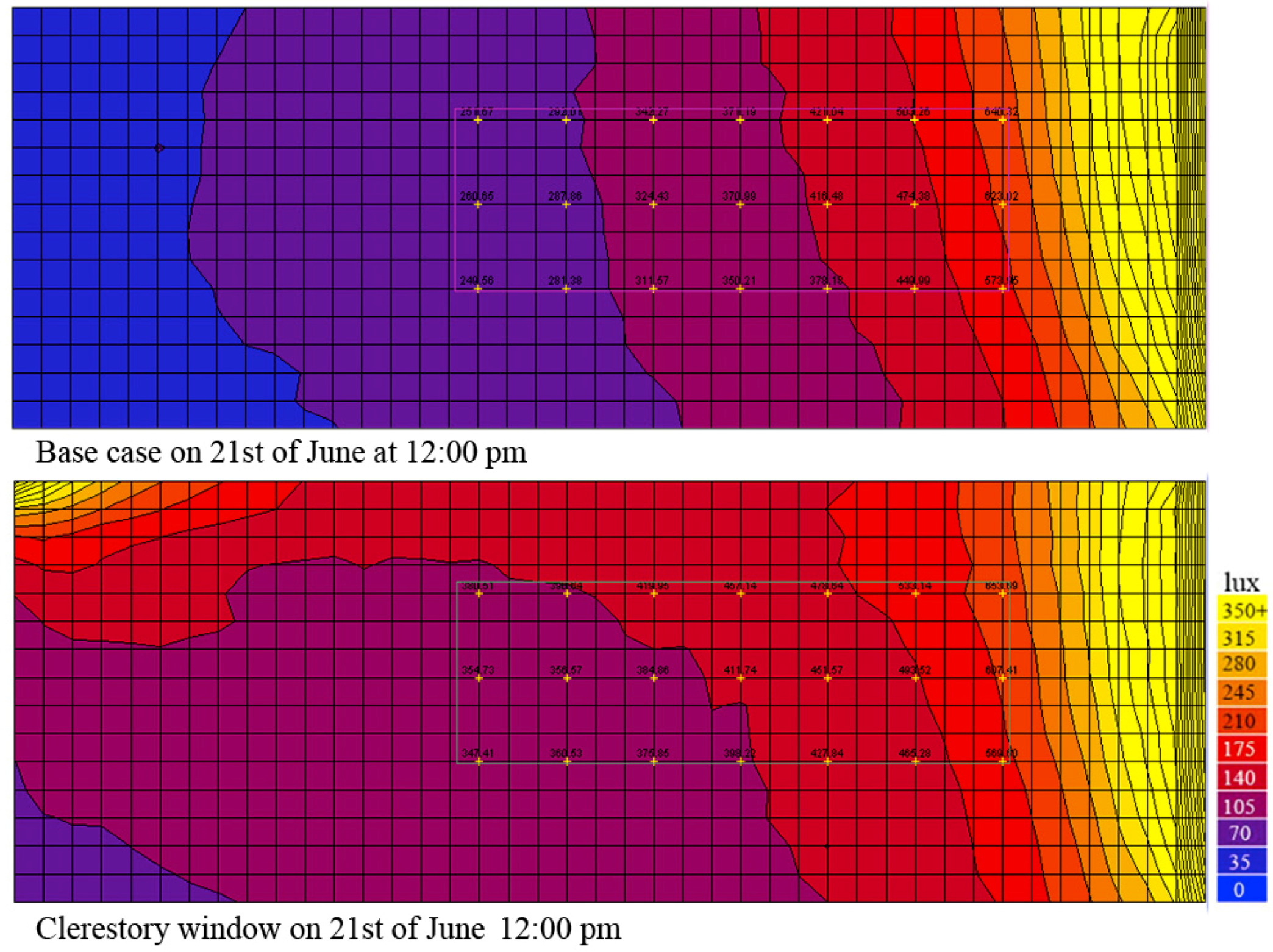
Whilst validation is important to show that the approach taken does not yield misleading results, the main aim of the comparative analysis was to gain a better understanding of where the implemented method diverges from others and why. The choice of daylight calculation method and its implementation within the prototype is described in detail as well as the process of comparing results against those of the same room configurations simulated in Radiance.

Radiance daylight software update#
This paper describes a prototype web-based tool that utilises WebGL and custom shaders to dynamically calculate the spatial distribution of daylight within a rectangular room and update it in real-time as the user interactively manipulates room dimensions, surface properties, window sizes and their positions within the envelope. Thus the primary goal is to undertake analysis that is fast enough to provide dynamic visual feedback during model manipulations and accurate enough for that feedback to be meaningful and useful. This work is part of ongoing research into the development of design tools that utilise analytical calculations performed on the graphics processing unit (GPU) to create highly dynamic and interactive building simulation environments. A detailed parametric comparison with Radiance simulations resulted in a small modifier to the implemented method that produces a robust correlation which the authors argue makes this tool a valuable educational resource with potential applications in early design decision-making. This tool\’s purpose is primarily educational, allowing users to gain a comprehensive understanding of the relationships between room dimensions, window placement and daylight distribution through a process of deliberate investigative play. This paper introduces a web-based daylighting simulation tool that does just that, using variants of the daylight coefficients and split-flux methods implemented on the GPU to calculate the real-time spatial distribution of daylight factors across a simple rectangular room. By investigating these and combining them with modern games technology, it is possible to create highly visual and interactive design tools that allow all the governing parameters of a simulation, including geometry, to be manipulated by the user in real-time with detailed contextual results updating dynamically with each interactive change. Whilst not all physical processes in the performance analysis of buildings can be simulated in real-time, some can. Research shows that real-time visual feedback can greatly assist the process of identifying and understanding complex cause and effect relationships. This report is a detailed supplement to the research paper titled " Dynamic Real-Time Daylight Simulation published in proceedings of the PLEA 2017 Conference in Edinburgh.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
